Water treatment
Water treatment
- Water sources that can be treated into domestic water
- Popular water treatment technologies today
- Standards for domestic water supply and calculation of domestic water supply flow
- WeMe’s project implementation process
- Water treatment technology solutions from WeMe
- Efficiency of the treatment process
- Subjects that can apply WeMe’s water treatment technology
- WeMe’s environmental services and commitments
Water sources that can be treated into domestic water
Currently, to treat water for domestic and production purposes, people can use input water sources such as: well water, underground water, surface water (from rivers, lakes), … The input indicators of these water sources often do not meet the requirements for domestic and production purposes:
Iron (Fe)
Exists in water in the form of Fe (II) or Fe (III). Groundwater has a high iron content and often exists in the form of Fe (II) dissolving bicarbonate, sulfate, chloride salts. Water with a high iron content often has a fishy smell; yellows clothes; damages products of the textile, paper, film, and canned food industries. Surface water contains Fe (III) in the form of organic colloids or suspended sediment, often has a low content and can be removed by iron combined with turbidity reduction technology.
Manganese (Mn)
Usually present in groundwater in the form of Mn (II) with a much lower content than iron. Manganese removal technology is often combined with iron removal in water.
Silicon acid compounds
Usually found in surface water in colloidal or soluble ion form depending on the pH of the water. High concentrations of silicic acid make it difficult to remove iron.
Nitrogen compounds
Exist in water in the form of nitrite, nitrate and ammonia. Nitrogen compounds in water indicate that the water has been contaminated by domestic wastewater.
Sulphate and chloride content
Exist in water in the form of sodium, calcium, magnesium salts and H2SO4, HCl acids. The high Cl– ion content in water (> 250 mg/L) makes the water taste salty. Groundwater sources with chloride content up to 500 – 1,000 mg/L can cause kidney disease. Water with high sulfate content (> 250 mg/L) is toxic to human health.
Iodine and fluoride
Commonly found in water in the form of ions and have a direct impact on human health.
Dissolved gases
O2, CO2, H2S gases in natural water fluctuate greatly. H2S gas is a product of the decomposition of organic matter. High H2S content in water makes water have an unpleasant rotten egg smell and corrodes metals. The dissolved O2 content in surface water is higher than in groundwater.
Microorganisms
In natural water, there are often many types of microorganisms that cause dangerous diseases such as: dysentery, typhoid, cholera, polio, …

Popular water treatment technologies today
The current water treatment process can apply the following common measures:
- Mechanical measures: using structures and equipment to clean water such as: trash screens, trash screens, settling tanks, filter tanks.
- Chemical measures: using chemicals added to water for treatment such as: using alum as a coagulant, using lime to alkalize water, adding chlorine to water for disinfection.
- Physical measures: using physical rays to disinfect water such as: ultraviolet rays, ultrasonic waves; electrolysis of seawater to desalinate; removing CO2 dissolved in water by aeration method.
Standards for domestic water supply and calculation of domestic water supply flow
According to TCXDVN 33:2006, the standard for total water use per capita includes water for: domestic drinking; industry; public works; watering plants; loss; … taken according to the table below:
| Water users | Water supply standards per capita (average day per year) L/person.day |
| Large cities, tourist and resort cities, large industrial parks | 300 – 400 |
| Medium and small cities, towns, small industrial parks | 200 – 270 |
| Towns, industrial-agricultural centers, industrial-fisheries centers, rural residential areas | 80 – 150 |
| Rural | 40 – 60 |
The method of calculating the domestic water supply flow is taken as an example for the project of Renovation, repair and upgrading of the water supply system for Cha Lo Border Gate Economic Zone implemented by WeMe. Based on the water usage standard of 100 – 150 L/person/day, the required water flow is presented specifically in the following table:
| Water use purpose | Unit | Quantity | Standard m3/person.day | Total capacity m3/day |
| Activities | Person | 3.453,3 | 0,130 | 448,92 |
| Watering plants, cleaning streets | m2 | 13,035 | 0,003 | 39,1 |
| Total | 488,02 | |||
| Reserve water, fire fighting | % | 20 | 97,60 | |
| Total | 585,63 |
Note: The amount of water used for fire prevention and fighting is taken as 20% of the total amount of water for domestic use, watering plants, and washing roads.
- Non-regulating coefficient for water for domestic use Kng = 1.2.
- Calculated water demand: 585.63 x 1.2 = 702.76 m3/day.
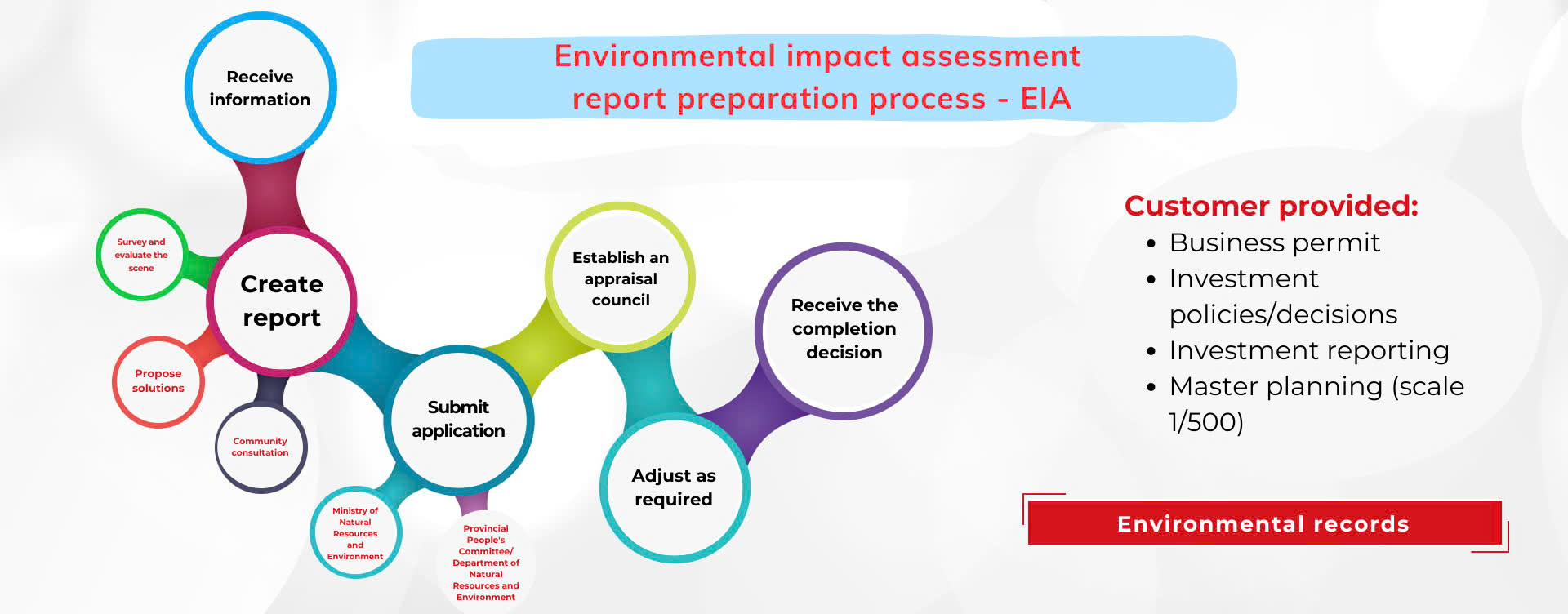
WeMe’s project implementation process
WeMe’s project implementation process for designing and constructing a water treatment system includes the following steps:
- Collect information, survey customers, analyze input water quality results, and develop a suitable technology plan to handle parameters exceeding the allowable limit.
- Quotation for items, signing of contracts.
- System design: detailed design of items to be constructed.
- Construction and installation of the system.
- System testing.
- Sampling and analysis of output water quality.
- Acceptance and putting into use.
Water treatment technology solutions from WeMe
Criteria for selecting water treatment technology
To select water treatment technology from surface water and groundwater, we need to consider the following criteria:
- Nature of the input water source: depending on the quality of the input water (surface water, groundwater, well water) and how many indicators exceed the permitted standards, we will choose the appropriate treatment technology.
- Technology treatment efficiency: ensure that input indicators exceeding the standards are brought back to the permitted values according to requirements.
- Saving construction area: the use of advanced technologies will optimize the treatment stage, helping to save area and investment and construction costs while still bringing high efficiency.
- Management, operation, and maintenance are suitable for the capacity of the investor.
- Reasonable investment costs, within the investor’s capacity.
- Safe, environmentally friendly.
- Easy to increase capacity or improve treatment efficiency in the future.
WeMe’s technology for treating water from surface water and groundwater
In cases where only simple indicators exceed the permitted standards
Description:
- The input water will be treated through 2 stages: disinfection and filtration.
- Disinfection cluster: chemicals are pumped directly from the chemical tank into the water pipe. Under the effect of the flow, the chemicals are mixed evenly in the water.
- Flocculation: add PAC and NaOH settling support chemicals into the pipe. PAC chemicals contain up to 28 – 32% aluminum, providing the ability to coagulate dirt in the water to support the filtration process effectively without harming the environment.
- Water filter column: retains suspended substances, insoluble substances, moss, etc. in the water source thanks to layers of filter materials. Quartz sand is used in water filtration technology to remove suspended solids, especially small particles that cannot precipitate when left to settle naturally. During the filtration process, a membrane will form on the surface of the filter tank. This is a layer of sediment that stabilizes the water flow after being filtered.
- The treated water meets QCVN 01-1:2018/BYT for domestic use.
In case many indicators exceed the permitted standards
In this case, WeMe will apply a technological solution using an aeration tower.
Description:
- Raw water from streams or wells is led to the treatment cluster and mixed with air through an oxidation tower to remove iron and remove CO2 in groundwater or oxidize organic substances in surface water.
- Then, the water flows down to the contact tank to ensure that the oxidation process completely reduces the amount of Fe (II). Here, PAC is added to the water to promote the coagulation and flocculation process.
- The water continues to flow into a vertical settling tank with a lamella settling plate. Here, the iron residue forms larger and larger flocs and settles in the settling tank, which will be periodically discharged. The clear water is collected in a sawtooth trough and flows to the filter tank.
- At the filter tank, the remaining residue in the water after settling will be retained through layers of filter material. The filter material includes: filter sand and a supporting gravel layer. The filtration speed is controlled through a concentric siphon system. Clean water after filtration is collected by a filter hood and then flows to the storage tank.
- At the storage tank, the water is disinfected with chlorine (powder form). Disinfectant water is distributed to the consumption network through the secondary pumping station. The water usage hours during the day are regulated by the inverter system.
- When the filter sand is covered with a lot of dirt, the filter process is clogged and the filter will be washed using the pure water washing method. The filter washing water and sedimentation tank discharge water are collected in the sludge settling tank.
WeMe’s water treatment projects
Here is information about some of the water treatment projects for domestic and production use that WeMe has implemented:
One One Joint Stock Company Central Project
- Address: Tam Vi Village, Loc Tien Commune, Phu Loc District, Thua Thien Hue Province, Vietnam
- Processing capacity: 500 m3/day.night
- Type of water supply: water supply for the factory’s production activities

Cha Lo Border Gate Economic Zone Project
- Address: Dan Hoa Commune, Minh Hoa District, Quang Binh Province
- Processing capacity: 720 m3/day.night
- Water supply type: domestic water supply.
Project of Poshaco Hung Yen Investment and Production Company Limited
- Address: Poshaco Hung Yen Investment and Production Company Limited, Tu Cau Village, Giai Pham Commune, Yen My District, Hung Yen Province
- Processing capacity: 240 m3/day.night
- Type of water supply: domestic and production water
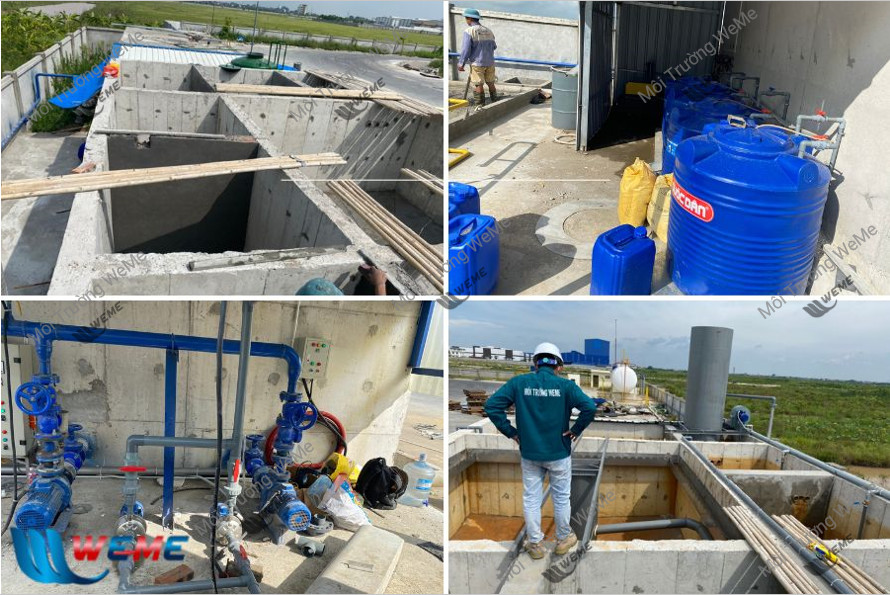

Efficiency of the treatment process
The output water after going through the water treatment process from WeMe’s surface water and groundwater sources is guaranteed to meet QCVN 01-1/2018/BYT with some of the following criteria:
| No. | Indicator | Unit | Input | Output QCVN 01-1/2018 /BYT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | pH | – | 6.88 | 6.0 – 8.5 |
| 2 | Total hardness (as CaCO3) | mg/L | 213 | 300 |
| 3 | Chloride (Cl–) | mg/L | 5.67 | 250 |
| 4 | Arsenic (As) | mg/L | Not detected LOD = 0.001 | 0.01 |
| 5 | Lead (Pb) | mg/L | Not detected LOD = 0.001 | 0.01 |
| 6 | Zinc (Zn) | mg/L | 0.170 | 2 |
| 7 | Iron (Fe) | mg/L | 5.95 | 0.3 |
| 8 | E. Coli | MPN/100 mL | Not detected LOD = 3.0 | < 1 |
Subjects that can apply WeMe’s water treatment technology
WeMe’s water treatment process from surface water and groundwater sources can be applied to many subjects that have different water treatment needs, such as:
- Enterprises, factories producing food, pharmaceuticals, beverages, etc.
- Factories, water supply stations for residents;
- …
WeMe’s environmental services and commitments
WeMe Energy Joint Stock Company is a unit that has been operating for many years in the environmental field. We have experience and expertise in many fields such as:
- Wastewater treatment
- Water supply treatment
- Environmental profile consulting
With the desire to bring many effective solutions in wastewater and water supply issues, WeMe always strives to improve service quality, bringing many advanced technologies at competitive prices in the market. WeMe is committed to the quality of our products, services and after-sales policies.

Customers who are looking for water treatment technology for domestic and production use, please contact us immediately for the most detailed advice and support. WeMe always wants to find customers across the country. Being with our customers is the pride of WeMe.